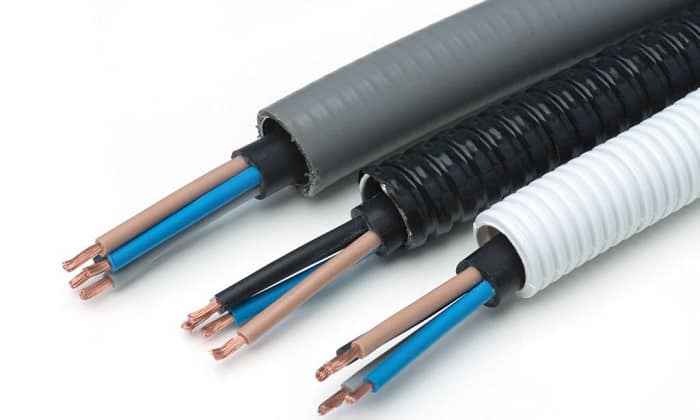
Conduits may provide protection for a 6/3 cable, and they can be used to bundle up multiple wires. However, to know what size conduit for 6/3 wire is best, we must look at the cross sectional area of the wire, the material, length, and width of the conduit.
For instance, the conduit size for 6/3 wire may be at least a 1” schedule 40 PVC. But this may vary depending on the conduit material.
Table of Contents
Different Types of Conduit
Several materials are available as conduits, and their use may vary, depending on the strength and stability of the material. We list some of the most common conduit materials here.
The first one is rigid PVC conduit. It is a non-metallic conduit that can be used in corrosive environments and direct burial, but it is not UV-stable, so it cannot be under direct sun exposure.
PVC can also make up a flexible conduit known as electrical non-metallic tubing or ENT. It can be used in concrete walls but not in exposed locations. Similar to rigid PVC, it is also not UV stable.
The next conduit material is electrical metal tubing or EMT. It may be made of steel or aluminum. It can be used in concrete but not in outdoor locations without additional modification.
Another metal conduit is the intermediate metal conduit or IMC. It is made out of steel and is thicker than EMT. It is also rated for outdoor use.
Then we have the rigid metal conduit or RMC. It is a heavy duty conduit made of steel or aluminum, and is strong but more expensive. It can be used to provide structural support to other electrical equipment.
Metal conduits can also come in the form of flexible metal conduits or FMC. These can be used around tight spaces and are commonly applied indoors.
Here is a list of the minimum conduit sizes for each material. These only apply to a 6/3 Romex cable in allowable locations and a 6/3 UF-B cable if necessary. See “Factors affecting conduit size” to check how these values were obtained.
| Material | Trade size for 6/3 Romex cable | Trade size for 6/3 UF cable |
| PVC Schedule 40 | 1 | 2 |
| ENT | 1 | 2 |
| EMT | 1 | 2 |
| IMC | 1 | 1 1/2 or 2 |
| RMC | 1 | 2 |
| FMC | 1 | 2 |
Factors Affecting Conduit Size
The US National Electric Code, or NEC, prescribes the proper conduit size for wires. The biggest factor that affects conduit size is the cross sectional area of the wire. The NEC prescribes the following:
- 1 cable or an individual conductor can fill up to 53% of the conduit only.
- 2 cables or individual conductors can fill up to 31% of the conduit only.
- More than 2 cables or individual conductors can fill up to 40% of the conduit only.
- A nipple (a wire that is not longer than 24 inches) can fill up to 60% of the conduit only.
Take note that a multiconductor cable is considered as a single conductor when determining the conduit fill size, whether it is for 6/2 Romex or for 6/4 wire. Also, the cross section of elliptical wires shall be based on their longest diameter and is to be calculated like a circle.
To determine the right electrical conduit size, we first determine the cross sectional area of the wire. The diameter of a Romex 6/3 wire with ground supplied by Southwire is 659 mills, or 0.659 inches. Thus, the cross sectional area of this wire is:
Since this is considered a single cable, then it should fill up to 53% of the conduit only (but if you want to add more conductors to the conduit in the future, then consider the other fill requirements). If it’s shorter than 24 inches, it can fill up to 60% of the conduit.
After calculating, we check chapter 9 of the electrical code for the conduit size chart based on the conduit material. If we want to use schedule 40 rigid PVC, we look at Chapter 9, Article 352 – Rigid PVC, Schedule 40.
Based on the chart, the right trade size, whether for a 53% fill or 60% fill, is at least 1” schedule 40 rigid PVC. This size can accommodate up to 0.441 in2 and 0.499 in2 respectively.
Tips to Determine Conduit Size
Know the uses of the wire
Always determine the rated uses of the wire to help verify the right conduit material. For instance, Romex is rated for indoor applications and is not for damp or wet locations, so leave this wire out when you size liquid tight for 6/3 wire conduits.
Whether a Romex 6/3 wire need to be in conduit indoors is a subject of debate. While it is not prohibited, some electricians do not recommend it.
Know the length of the wire
Remember that a nipple can take up to 60% fill in the conduit. Any setups longer than 24 inches must consider other fill requirements.
Know if the cable is a multiconductor one.
When calculating for the cross sectional area, 6/3 multi-conductors’ conduit size is not the same as 3 individual 6 gauge wire conduit size. The extra sheathing of 6/3 cables needs to be considered in the cross sectional area for the right conduit fill.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does a 6/3 wire need to go in the conduit?
Not all of the time. Cables rated for their purposes have respective sheathing that satisfies NEC requirements, like Romex 6/3 cables for indoor use, but conduits can protect cables when they are exposed to conditions that can damage the wires.
However, always check your local code for applications that need conduits.
How many wires can I put in a 1 inch conduit?
The material and the wire gauge need to be considered. 1-inch EMT, IMC, and RMC may fit up to seven individual 6-gauge wires, while 1-inch schedule 40 rigid PVC can fit six. This is only true for 6 gauge wire.
Multiconductor cables are a different story. It’s best to use the method above to determine the right conduit size. A Romex conduit fill chart is not directly available, so it’s nice to know the cross sectional area instead.
Conclusion
Different conduits can have varying fill requirements, but the cross sectional area of the wire must be considered when determining what size conduit for 6/3 wire to use. The NEC prescribed these fill requirements for electrical safety in residences.
While a 1” schedule 40 rigid PVC is enough for a 6/3 wire, other materials may need larger or smaller trade sizes. It’s always good to refer to the NEC and the local code to properly protect the cables using conduits.
A Recommended guide for you: Steps to connect PVC conduit to an electrical box

I am Edwin Jones, in charge of designing content for Galvinpower. I aspire to use my experiences in marketing to create reliable and necessary information to help our readers. It has been fun to work with Andrew and apply his incredible knowledge to our content.